前言
前一段时间风风火火的Spring RCE,看起来限制条件还是挺多的,学习一下。
环境搭建
漏洞信息,要求在JDK9+的环境下在Tomcat部署war包,如果是通过SpringBoot可执行Jar文件的方式部署则漏洞不可用,但不排除有更多方法可以完成利用。
先搞个Spring MVC方便利用,使用IDEA新建项目:
再添加依赖:
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
|
新建控制器包com.example.controller,里面放一个IndexController控制器:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| package com.example.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index() {
return "index";
}
}
|
新建resources文件夹,在resources文件中新建spring config文件spring-mvc.xml:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.example.controller"/>
<bean id="internalResourceViewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
</bean>
</beans>
|
在WEB-INF下新建views文件夹,里面放一个index.jsp模板文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Index</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Index</h1>
</body>
</html>
|
最后修改web.xml:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| <!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
|
配置war部署,看到控制器运行结果:

接下来开始布置漏洞环境,在com.example包下新建一个model包,放一个有基础getter和setter的POJO类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| package com.example.model;
public class User {
private long id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String email;
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String toString() {
return "[Username: " + username + ", Password: " + password + ", Email: " + email + "]";
}
}
|
然后修改一下控制器:
1
2
3
4
5
| @RequestMapping("/user")
public String user(User user) {
System.out.println(user);
return "user";
}
|
可以看到对象绑定成功了:
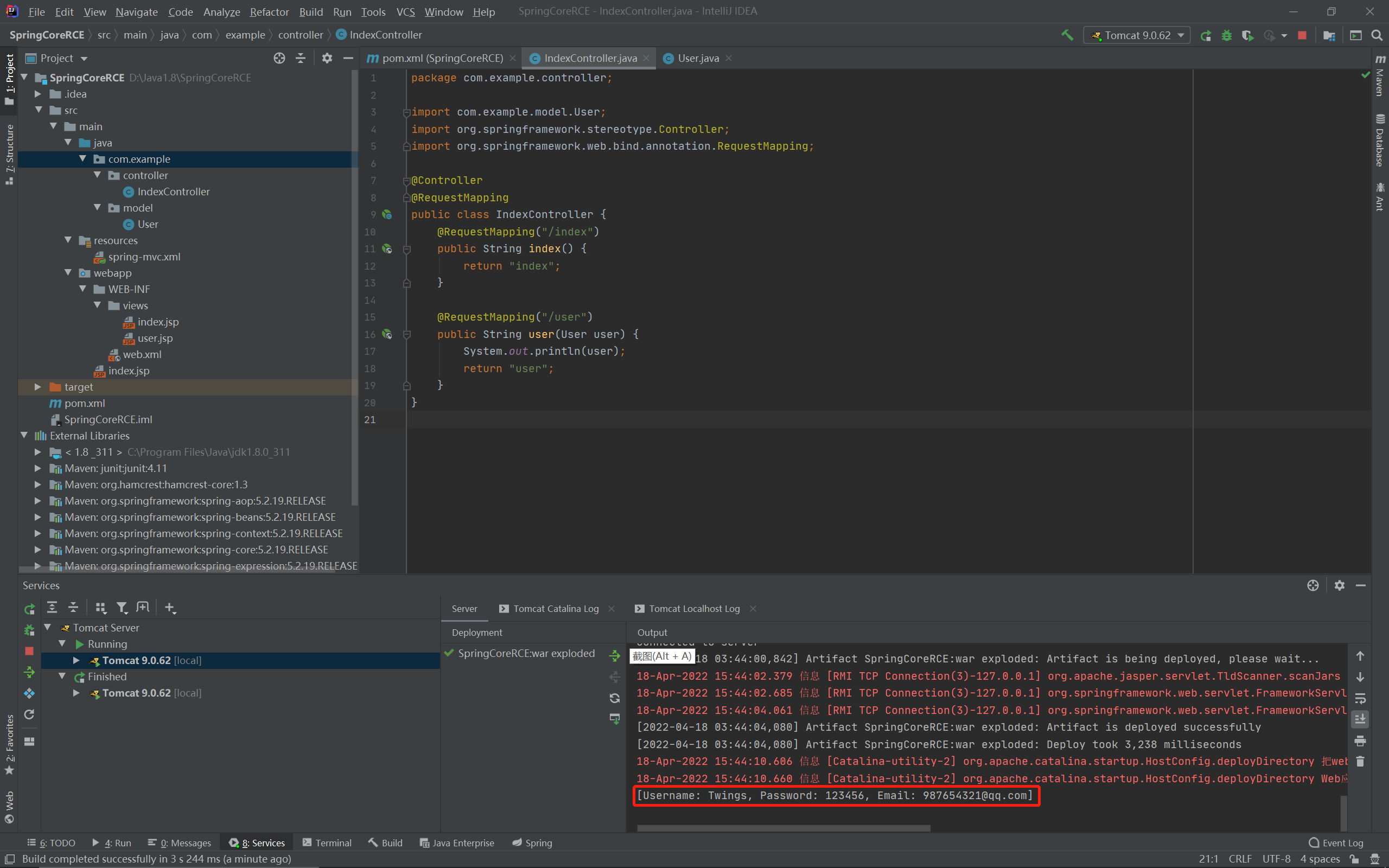
漏洞分析
给User类中的setter下一个断点,看看他的对象绑定是如何进行的,从dobind开始找到AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor类的setPropertyValue函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public void setPropertyValue(PropertyValue pv) throws BeansException {
AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor.PropertyTokenHolder tokens = (AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor.PropertyTokenHolder)pv.resolvedTokens;
if (tokens == null) {
String propertyName = pv.getName();
AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor nestedPa;
try {
nestedPa = this.getPropertyAccessorForPropertyPath(propertyName);
}
...
tokens = this.getPropertyNameTokens(this.getFinalPath(nestedPa, propertyName));
if (nestedPa == this) {
pv.getOriginalPropertyValue().resolvedTokens = tokens;
}
nestedPa.setPropertyValue(tokens, pv);
} else {
this.setPropertyValue(tokens, pv);
}
}
|
此时的参数pv:
即我们输入的email,下一步就是获取这些数据要赋值到什么属性里去,跟入getPropertyAccessorForPropertyPath函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| protected AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor getPropertyAccessorForPropertyPath(String propertyPath) {
int pos = PropertyAccessorUtils.getFirstNestedPropertySeparatorIndex(propertyPath);
if (pos > -1) {
String nestedProperty = propertyPath.substring(0, pos);
String nestedPath = propertyPath.substring(pos + 1);
AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor nestedPa = this.getNestedPropertyAccessor(nestedProperty);
return nestedPa.getPropertyAccessorForPropertyPath(nestedPath);
} else {
return this;
}
}
|
然后会判断属性名中是否存在.[]等字符,将属性名按.切成两半,前半作为参数调用调用getNestedPropertyAccessor,修改一下输入的属性名加个.再重开调试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| private AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor getNestedPropertyAccessor(String nestedProperty) {
if (this.nestedPropertyAccessors == null) {
this.nestedPropertyAccessors = new HashMap();
}
AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor.PropertyTokenHolder tokens = this.getPropertyNameTokens(nestedProperty);
String canonicalName = tokens.canonicalName;
Object value = this.getPropertyValue(tokens);
...
AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor nestedPa = (AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor)this.nestedPropertyAccessors.get(canonicalName);
if (nestedPa != null && nestedPa.getWrappedInstance() == ObjectUtils.unwrapOptional(value)) {
...
} else {
...
nestedPa = this.newNestedPropertyAccessor(value, this.nestedPath + canonicalName + ".");
...
}
return nestedPa;
}
|
可以看到value是个Object对象,最后会放入nestedPa中返回,看起来是对象绑定的主体,跟入getPropertyValue:
1
2
3
| String propertyName = tokens.canonicalName;
String actualName = tokens.actualName;
AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor.PropertyHandler ph = this.getLocalPropertyHandler(actualName);
|
调用getLocalPropertyHandler获取属性处理对象,再跟入:
1
2
3
4
| protected BeanWrapperImpl.BeanPropertyHandler getLocalPropertyHandler(String propertyName) {
PropertyDescriptor pd = this.getCachedIntrospectionResults().getPropertyDescriptor(propertyName);
return pd != null ? new BeanWrapperImpl.BeanPropertyHandler(pd) : null;
}
|
getCachedIntrospectionResults会依据User类新建一个处理对象返回:
1
2
3
4
| results = new CachedIntrospectionResults(beanClass);
...
CachedIntrospectionResults existing = (CachedIntrospectionResults)classCacheToUse.putIfAbsent(beanClass, results);
return existing != null ? existing : results;
|
CachedIntrospectionResults的构造函数中调用getBeanInfo获取对象属性信息:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| private static BeanInfo getBeanInfo(Class<?> beanClass) throws IntrospectionException {
Iterator var1 = beanInfoFactories.iterator();
BeanInfo beanInfo;
do {
if (!var1.hasNext()) {
return shouldIntrospectorIgnoreBeaninfoClasses ? Introspector.getBeanInfo(beanClass, 3) : Introspector.getBeanInfo(beanClass);
}
BeanInfoFactory beanInfoFactory = (BeanInfoFactory)var1.next();
beanInfo = beanInfoFactory.getBeanInfo(beanClass);
} while(beanInfo == null);
return beanInfo;
}
|
来到Java内部Introspector类的getBeanInfo函数中,除了获取对象自身的属性信息,还会去找父类的属性信息,于是在找父类java.lang.Object的属性信息时调用的getTargetPropertyInfo函数中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| if (argCount == 0) {
if (name.startsWith(GET_PREFIX)) {
pd = new PropertyDescriptor(this.beanClass, name.substring(3), method, null);
} else if (resultType == boolean.class && name.startsWith(IS_PREFIX)) {
pd = new PropertyDescriptor(this.beanClass, name.substring(2), method, null);
}
}
|
如果存在isXXX和getXXX就会将后面的部分作为一个属性,也就导致了User类多了个叫做class的属性,也就导致了在getPropertyDescriptor函数中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| PropertyDescriptor getPropertyDescriptor(String name) {
PropertyDescriptor pd = (PropertyDescriptor)this.propertyDescriptors.get(name);
if (pd == null && StringUtils.hasLength(name)) {
pd = (PropertyDescriptor)this.propertyDescriptors.get(StringUtils.uncapitalize(name));
if (pd == null) {
pd = (PropertyDescriptor)this.propertyDescriptors.get(StringUtils.capitalize(name));
}
}
return pd;
}
|
而propertyDescriptors中除了我们定义的4个属性的描述符外还有一个奇怪的东西:
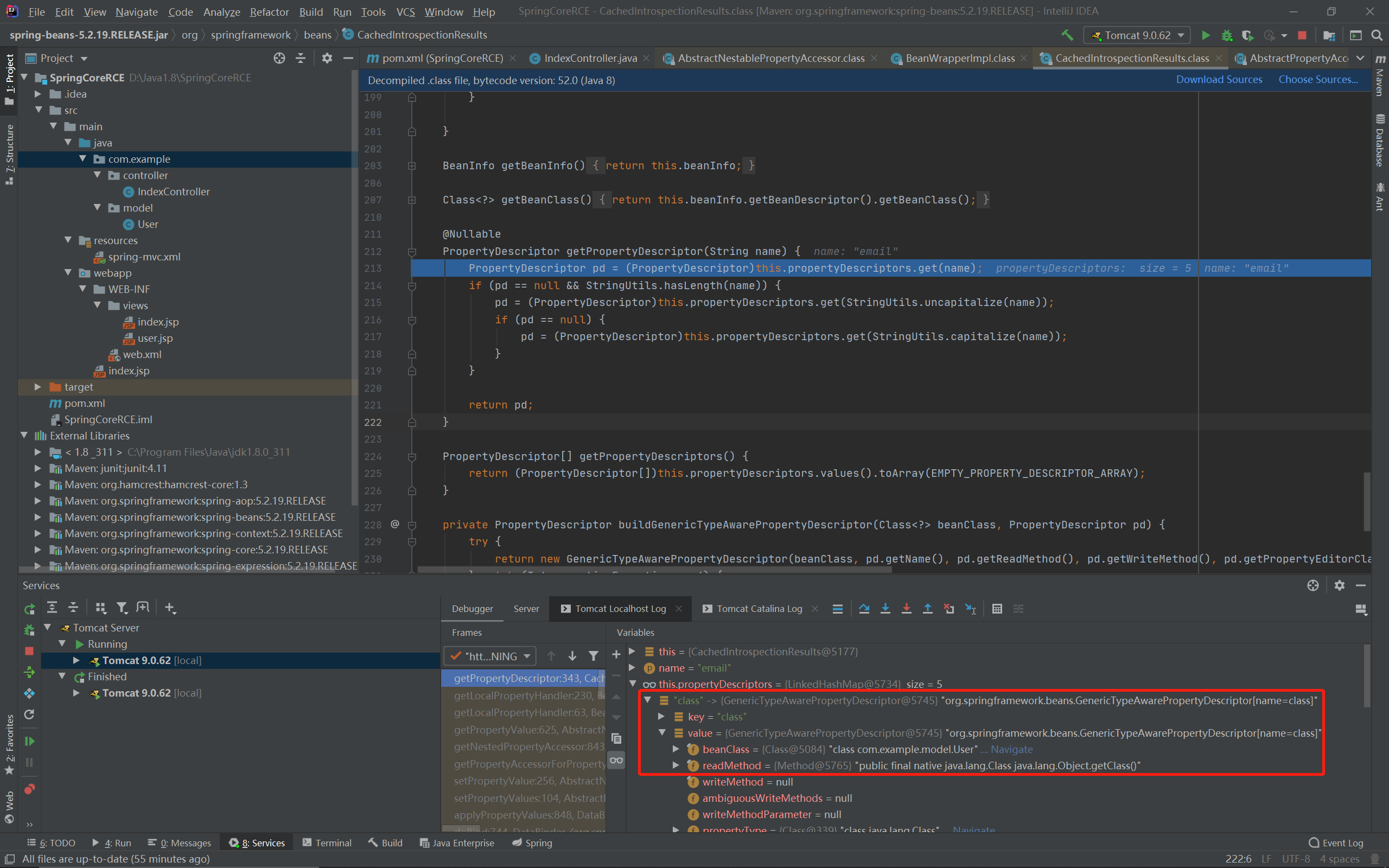
其getter为getClass,也就是说我们可以通过class.xxx访问user.getClass.xxx:
漏洞利用
在JDK9+环境下,getTargetPropertyInfo的属性信息从缓存中获取:
1
| Map.Entry<String,PropertyInfo> entry : ClassInfo.get(this.beanClass).getProperties().entrySet()
|
ClassInfo的get函数如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public static ClassInfo get(Class<?> type) {
if (type == null) {
return DEFAULT;
}
try {
checkPackageAccess(type);
return CACHE.get(type);
} catch (SecurityException exception) {
return DEFAULT;
}
}
|
最后从CACHE中取出该类的属性信息,CACHE在项目运行时开始构建,最后来到PropertyInfo类的get函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| switch (method.getParameterCount()) {
case 0:
if (returnType.equals(boolean.class) && isPrefix(name, "is")) {
PropertyInfo info = getInfo(map, name.substring(2), false);
info.read = new MethodInfo(method, boolean.class);
} else if (!returnType.equals(void.class) && isPrefix(name, "get")) {
PropertyInfo info = getInfo(map, name.substring(3), false);
info.readList = add(info.readList, method, method.getGenericReturnType());
}
break;
case 1:
if (returnType.equals(void.class) && isPrefix(name, "set")) {
PropertyInfo info = getInfo(map, name.substring(3), false);
info.writeList = add(info.writeList, method, method.getGenericParameterTypes()[0]);
} else if (!returnType.equals(void.class) && method.getParameterTypes()[0].equals(int.class) && isPrefix(name, "get")) {
PropertyInfo info = getInfo(map, name.substring(3), true);
info.readList = add(info.readList, method, method.getGenericReturnType());
}
break;
case 2:
if (returnType.equals(void.class) && method.getParameterTypes()[0].equals(int.class) && isPrefix(name, "set")) {
PropertyInfo info = getInfo(map, name.substring(3), true);
info.writeList = add(info.writeList, method, method.getGenericParameterTypes()[1]);
}
break;
}
|
根据函数参数数量获取参数,比JDK8+更复杂获取的结果也更多了,原本这里是有classLoader的:
但是回到CachedIntrospectionResults类的构造函数函数后,它会遍历所有属性信息,然后:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| if (Class.class != beanClass || !"classLoader".equals(pd.getName()) && !"protectionDomain".equals(pd.getName())) {
...
pd = this.buildGenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor(beanClass, pd);
this.propertyDescriptors.put(pd.getName(), pd);
}
|
将Class中的classLoader给吃掉了,所以无法直接通过class.classloader来获取classloader。
但是Class中存在module:
1
| private final ClassLoader loader;
|
可以通过class.module.classLoader获得一个classloader:
class.module.classLoader.resources.context获取Tomcat的context时问题又来了,我使用的Tomcat版本为9.0.62,该版本下的getResources函数为:
1
2
3
4
5
|
@Deprecated
public WebResourceRoot getResources() {
return null;
}
|
已经被废弃了,无法获取resources。
没办法,再下载多一个Tomcat8.0.53,其getResources为:
1
2
3
| public WebResourceRoot getResources() {
return this.resources;
}
|
还是可以利用的,所以这payload在高版本Tomcat下面也打不通,但不排除还有其他玩法。
最后打法可以看参考文章,通过修改日志文件目录和后缀的方式完成getshell。
漏洞修复
在5.2.20.RELEASE版本下,CachedIntrospectionResults类的构造函数做了更多限制:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| PropertyDescriptor pd = var3[var5];
if ((Class.class != beanClass || "name".equals(pd.getName()) || pd.getName().endsWith("Name")) && (pd.getPropertyType() == null || !ClassLoader.class.isAssignableFrom(pd.getPropertyType()) && !ProtectionDomain.class.isAssignableFrom(pd.getPropertyType()))) {
...
pd = this.buildGenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor(beanClass, pd);
this.propertyDescriptors.put(pd.getName(), pd);
}
|
无法获取类型为ClassLoader的属性了。
参考
https://www.cnblogs.com/chenty/p/14373273.html
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzI3MTQyNzQxMA==&mid=2247484800&idx=1&sn=06dd94d84f5fdd24f9e1a2b95d896a8a&chksm=eac0b7bdddb73eab4cc0225c38646d57cd17a668700a95e9d57f1f369db6a0ade9a003d9fd39&mpshare=1&scene=2&srcid=0401971aXDidTqenAU9KC0Ct&sharer_sharetime=1648820954447&sharer_shareid=3ca7aa86b51d7b96de87c8f2d9956820&from=timeline#rd







